
Built from high-quality optics, the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples provides higher clarity for scientific and educational use. The durable body provides stable operation, and the adjustable head and stage setup provide ergonomic convenience. Advanced illumination systems enable observation with high contrast of transparent and reflected samples. The microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples is compatible with digital cameras and display devices, enabling real-time observation and recording of microscopic structures for further study and analysis.

The microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples is applied widely in biology for studying cells, tissues, and microorganisms with unmatched clarity. Clinically, it is applied to assist in the diagnosis of infections, blood diseases, and cell disorders. In industry, the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples is employed for material examination, surface flaw detection, and microstructure analysis of metals and polymers. In institutions of learning, it is a teaching tool that helps students learn microscopic anatomy and chemical reactions. Its use extends into environmental monitoring where it is used to analyze soil or water samples to ascertain quality and detect pollutants.
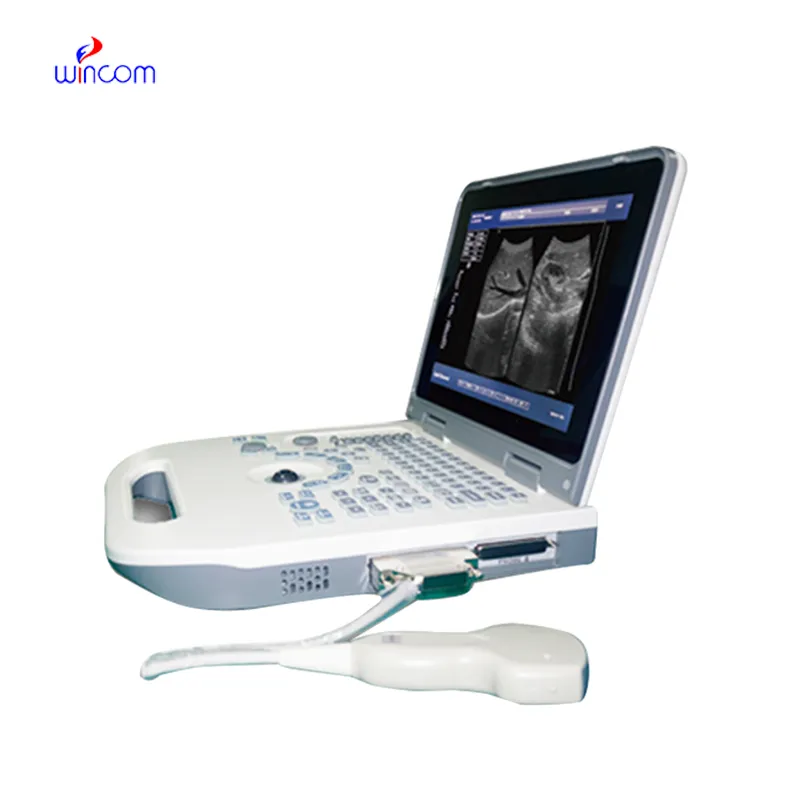
With the progress of technology, the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples will turn into a smarter and more interactive research tool. Compatibility with AI will allow it to detect patterns, recognize anomalies, and measure data automatically. The microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples will also make remote diagnostics possible, where the samples from every corner of the world can be diagnosed remotely by specialists. Advances in imaging sensors and optical systems will provide better depth resolution and faster capture rates. These will expand the uses of the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples in medicine, nanotechnology, and education.

Users should implement a routine maintenance plan to ensure the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples remain in excellent working condition. Clean all optical parts using a blower or soft brush initially before a thorough cleaning. Do not disassemble the instrument at any time save by qualified individuals. Use light lubricant on moving parts to prevent stiffness and wear. The microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples should be kept in a chemical fume and moisture-free environment. Power cables and lighting systems should be checked regularly for signs of premature deterioration or breakdown.
With a microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples, human man can explore the microcosm with unprecedented clarity. The instrument magnifies small samples so that exact study can be conducted in laboratories, clinics, and schools. The microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples recognizes cell morphology, bacterial cultures, and intricate material surfaces. Although optical and electronic technology has been enhanced, the microscope for observing microorganisms in water samples of today's time offers more magnification, image stability, and integration into digital media for efficient data registration and perception.
Q: What is a microscope used for? A: A microscope is used to magnify tiny objects or structures, allowing detailed observation of cells, microorganisms, and materials that are invisible to the naked eye. Q: How often should a microscope be calibrated? A: To maintain measurement accuracy and ensure accurate focus during research or analysis, regular calibration should be performed, typically once or twice a year. Q: What type of light source is commonly used in a microscope? A: Most modern microscopes use LED or halogen light sources, which provide stable light and adjustable brightness for clear images at a wide range of magnifications. Q: Can a microscope be connected to a computer? A: Yes, many microscope models feature USB or HDMI ports that allow image capture and digital display through specialized imaging software. Q: How should a microscope be stored when not in use? A: A microscope should be covered with a dust shield and stored in a cool, dry location to prevent contamination and protect optical components from humidity.
The delivery bed is well-designed and reliable. Our staff finds it simple to operate, and patients feel comfortable using it.
I’ve used several microscopes before, but this one stands out for its sturdy design and smooth magnification control.
To protect the privacy of our buyers, only public service email domains like Gmail, Yahoo, and MSN will be displayed. Additionally, only a limited portion of the inquiry content will be shown.
I’m looking to purchase several microscopes for a research lab. Please let me know the price list ...
We are planning to upgrade our imaging department and would like more information on your mri machin...
E-mail: [email protected]
Tel: +86-731-84176622
+86-731-84136655
Address: Rm.1507,Xinsancheng Plaza. No.58, Renmin Road(E),Changsha,Hunan,China